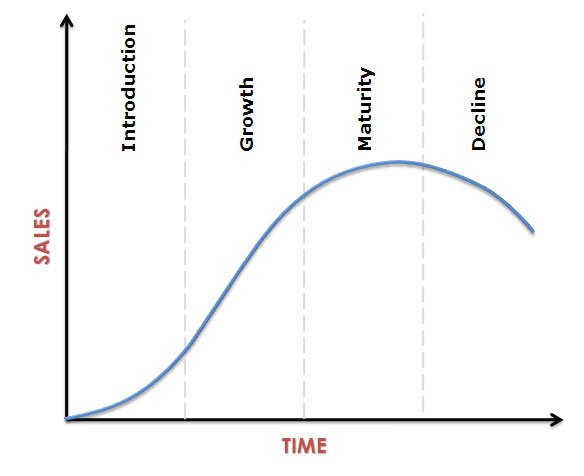
Product Life Cycle:
The period over which a product is developed, brought to market and eventually removed from the market. First, the idea for a product undergoes research and development. If the idea is determined to be feasible and potentially profitable, the product will be produced, marketed and rolled out. Assuming the product becomes successful, its production will grow until the product becomes widely available. Eventually, demand for the product will decline and it will become obsolete.
A marketing theory in which products or brands follow a sequence of stages including: introduction, growth, maturity, and sales decline.
Distinct stages in Product life cycle:
Product passes through distinct stages during its life & is called product life cycle. The product life cycle is normally presented as a sales curve spanning the products course from introduction to exit. The product life cycle concept says that each stage in the cycle is characterized by a typical marketer behaviour & each stage leads to a distinctive marketing strategy.
Product passes through 4 stages:
- Introduction
- Growth
- Maturity
- Decline
Introduction Stage:
The product is in introductory stage. At this stage, there may not be a ready market for the product. Sales are low. Profit seems a remote possibility, demand should be created and developed. Consumers should be prompted to try out the product. One of the crucial decisions to be taken in this stage is the pricing strategy to be adopted either market skimming or market penetration. Skimming strategy involved high price, taking advantage of early entry & the novelty of the product.
Penetration pricing involves low prices with a view to having a good market coverage. It also aims at keeping the competition out.
Growth Stage:
During the market growth stage, demand for the product increases & size of market grows. The sales & profits also go up. But by the time the marketer settles down with his product, competitors may enter the scene with similar or slightly improved versions. The marketer should stay ahead of his competitor & should reconsider his pricing strategy. He follows competition oriented pricing, because the total market is being shared among many firms. Marketing & distribution efficiency becomes decisive factor at this state.
Maturity Stage:
In the maturity stage, the demand tends to reach a saturation point & there is enough supply from competitive sources. Price competition becomes intense & exploits the brand loyalty. The marketer tries out product & packaging modification, & promotional. Deals & make special offers to new market segments so that his sales volume does not shrink. Long term and short-term marketing plans are implemented to profitably prolong the maturity stage.
Decline Stage:
In the decline stage, sales begin to fall. The demand for the product shrinks, probably due to new & functionally advanced products, becoming available in the market. The prices & margins get depressed, total sales & profits diminish. But some firms at this stage may try to link up the sales of these products with some other premium products they have developed & thus try to stretch the life of the decline product.
Thus, Product life cycle concept helps and is used as a tool in formulating and implementing marketing strategy.
- It facilitates pre-planning the product launch.
- Facilitates prolonging the profitable phase.
- Facilitates investment decisions on products.
- Facilitates choice of appropriate entry strategy.
- Facilitates choice of the right time to exit.
- Provides useful clues for managing customers.
January 03, 2018